Displaying items by tag: Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta
It was with the numerous J/109s in IRC 1 that blood was on the bay today at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta, with the narrow overnight lead of Outrajeous (Richard Colwell & John Murphy) snatched away by a final win by John Maybury’s Joker 2, where the input from Killian Collins of Crosshaven was clearly no hindrance.
Outrajeous had a day to forget as quickly as possible, as she slipped to 10th and thus had to carry a previously discarded 9th from the first race on Thursday. Thus she found herself back in 4th overall - just one sneeze in this red-hot class knocks your placing awry. The Goodbody family in White Mischief took second overall with 15 points while Joker 2 had 12, making it Top Two for the RIYC, and Pat Kelly’s Storm slipped past Outrajeous to grab third OA on 16.
Storm also held onto the lead in the RC35 division, well clear of the Hall family in Something Else (NYC) at second, while Debbie & Kevin Aitken in the First 36.7 Animal from Scotland took third.
In a summer of achievements for John Maybury, his Class One defence follows four consecutive class wins of IRC National Championship victories, the 2019 win coming on Dublin Bay last month. Today's victory was Maybury's fifth VDLR class win in a row winning first in 2011.
Seamus Fitzpatrick’s elegant First 50 Mermaid IV (RIYC) was back on form today to win the IRC Coastal Division of Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta today and thus was able to discard yesterday’s unwelcome 11th to put her into the overall lead and first in Division A with three bullets. Peter Dunlop from Pwllheli with the J/109 Mojito has discarded today’s sixth to place him second overall in the complete class, and he remains as leader in Division B.
In Division A, George Sisk’s Xp 44 WOW is second and Glynn Sheffield’s Farr 40 Espresso Martine Too from West Lancs YC is third while in Div B Mojito leads from sister-ship Jet Stream (Nigel Ingrams, Holyhead SC) with the J/97 Windjammer (Lindsay Casey & Denis Power, RStGYC) in third.
There were coastal fleet grumblings following today's coastal course when 17 in the fleet, mostly lower-rated boats, timed out and didn't get a finish due to the prevailing light airs.
It means today's coastal race counts for the first 11 but 17 boats counted maximum points for race four.
'Eleuthera' Ties the Knot in Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta IRC Zero as 'Signal 8' Finally Gets a Win
Jamie McWilliam's Ker 40 Signal 8 from Hong Kong may have found all the pieces were falling into place on this last outing at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta today as she took her first win of the series in IRC Zero but Frank Whelan’s Grand Soleil 44 from Greystones with Shane Hughes on the strength was never far off the pace, and took a useful second to have her first overall on 7 points to the 12 of Jay Colvillle’s First 40 Forty Licks (East Down YC), while Signal took third OA on 14.
There’s a finishing buoy in there somewhere (see above) as Hal Sisk in Colleen Ban (26) chases Dermot O’Flynn in Colleen Deas (28) for the final few yards in the first racing for Colleens in Dublin Bay in 114 years.
Perhaps they'd a special name for this tactical ploy back in the golden days just before the Great War obliterated much of the sailing scene, but it looks to us (see below) as though an impressive amount of thought is going to attach to whether or not Colleen Deas has actually gybed onto starboard, surely she should have held her course anyway, and beyond that there’s all the usual stuff about overtaking boat keeping clear etc etc etc……

George Kingston has won the Laser Standard division of the prestigious 2019 Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta by seven clear points overall.
The Cork native led the 11-boat series from Thursday's first race and counts five race wins from seven sailed.
As Afloat reported previously, the Royal St George sailor gave a masterclass in race management and consistency last weekend when he strolled to the Laser Leinster title in the waters off Rush.
Second overall is Kingston's clubmate Ross O'Leary with a third Royal St George sailor, Gavan Murphy, the Dun Laoghaire Laser Class Captain in third.
Mullaghmore Old Gaffer 'Purple Haze' Tops Thriving Classic Keelboat Fleet at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta
The Mullaghmore Sailing Club Old Gaffer 'Purple Haze' skippered by Kevin and Heather Collins leads a 12-boat Classic Keelboat fleet at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta.
Born out of 2017's Dun Laoghaire Harbour bicentenary celebrations, the 2019 classic keelboat fleet includes three gaff-rigged Colleen replicas that is reckoned to be the first time in 114 years that the J E Doyle-designed Colleen ODs had raced as a class in Dublin Bay.
David William's Colleen Eile is second overall with David Espey's restored Dublin Bay 24 Periwinkle lying third.
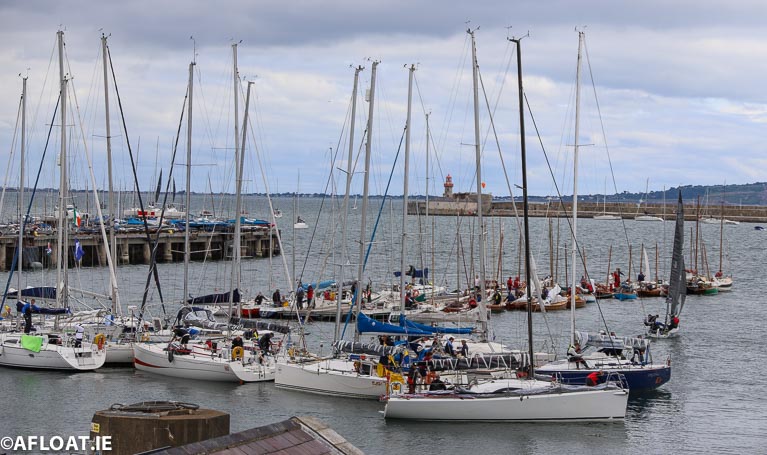 The Classic fleet is moored for the regatta at an innovative pontoon extension at the National Yacht Club alongside other traditional classes
The Classic fleet is moored for the regatta at an innovative pontoon extension at the National Yacht Club alongside other traditional classes
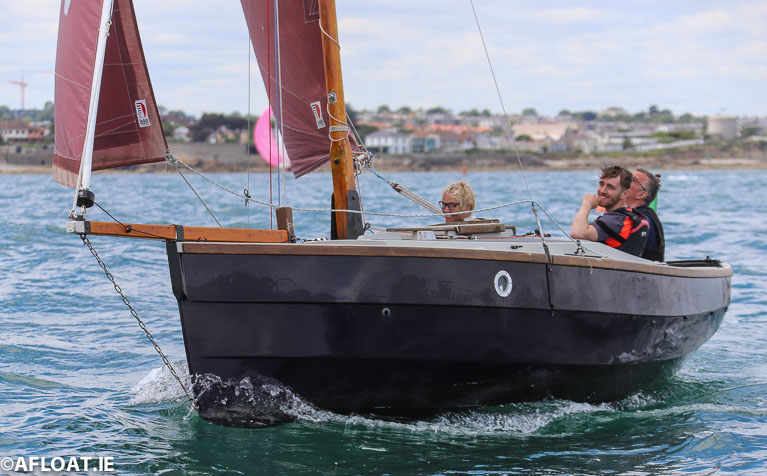 Above and below Kevin & Heather Collins' Purple Haze from Mullaghmore Sailing Club
Above and below Kevin & Heather Collins' Purple Haze from Mullaghmore Sailing Club
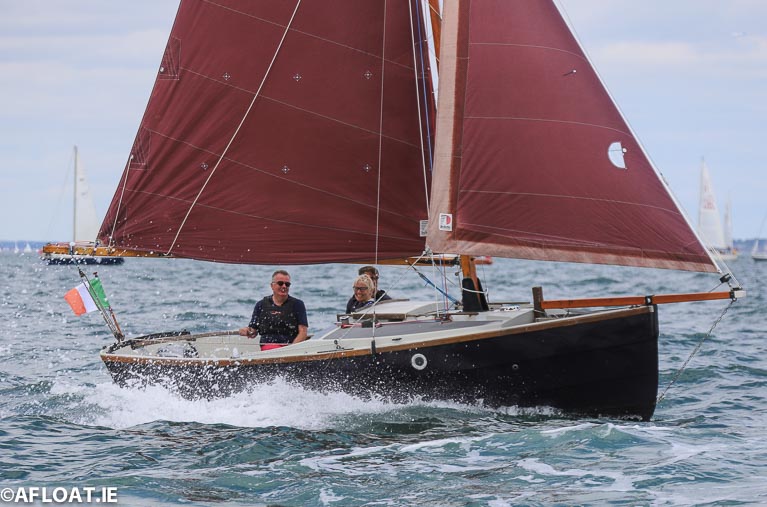
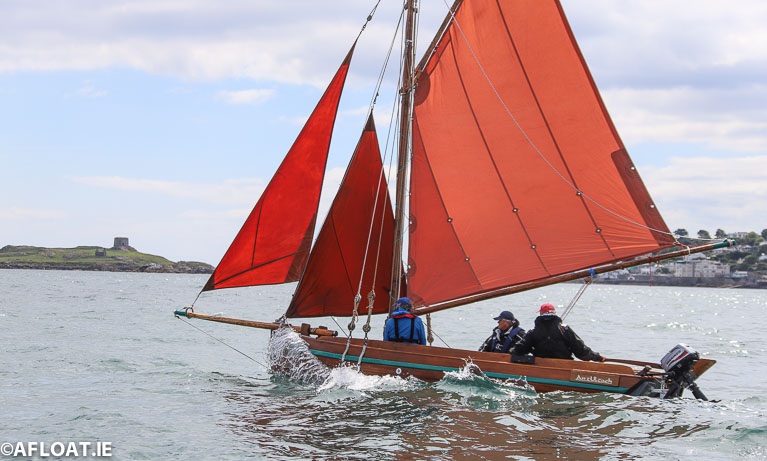

 Tom Fitzpatrick's an tUltach from Howth Yacht Club
Tom Fitzpatrick's an tUltach from Howth Yacht Club
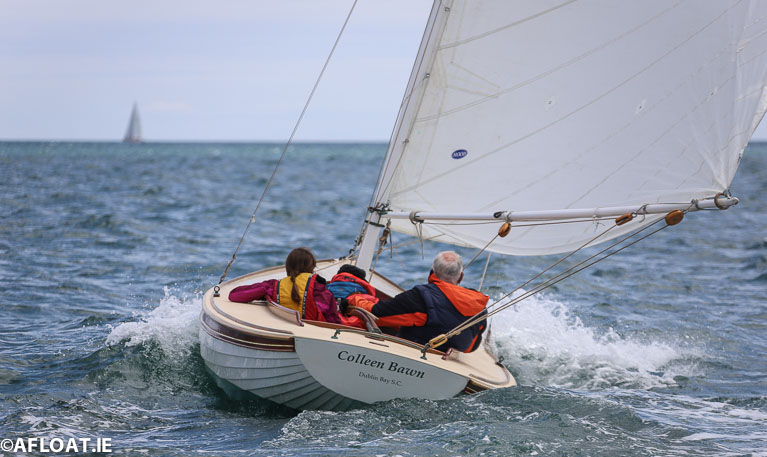 Hal Sisk's Colleen Bawn from the Royal Irish Yacht Club
Hal Sisk's Colleen Bawn from the Royal Irish Yacht Club
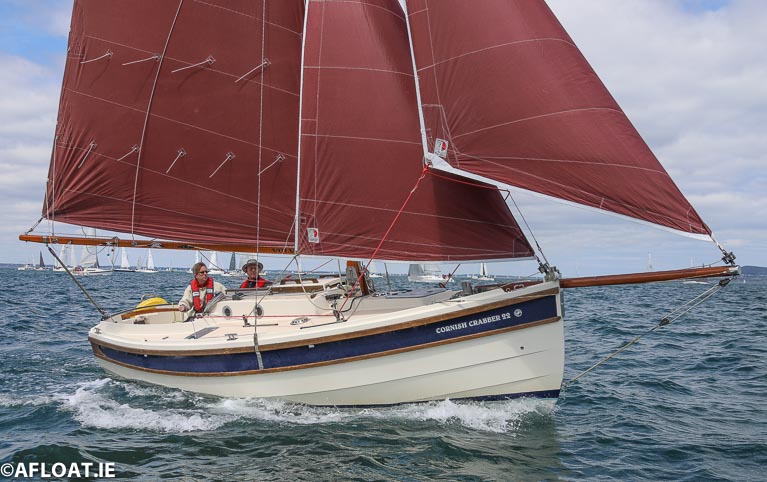 Dennis Aylmer's Mona from the Royal Irish Yacht Club
Dennis Aylmer's Mona from the Royal Irish Yacht Club
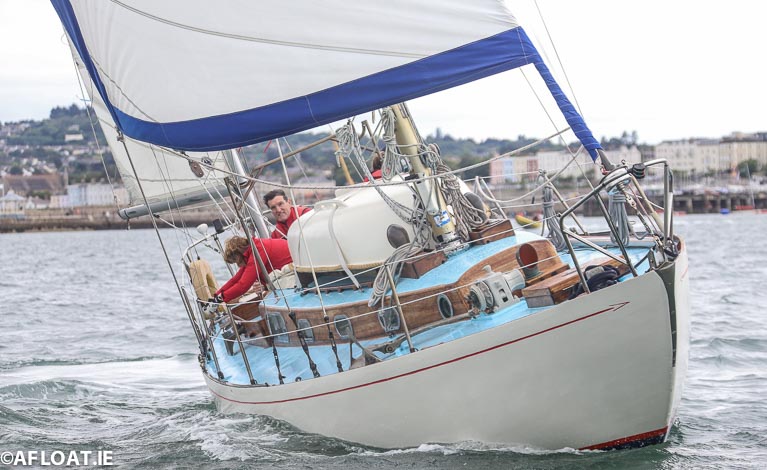 Verve from the Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club
Verve from the Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club
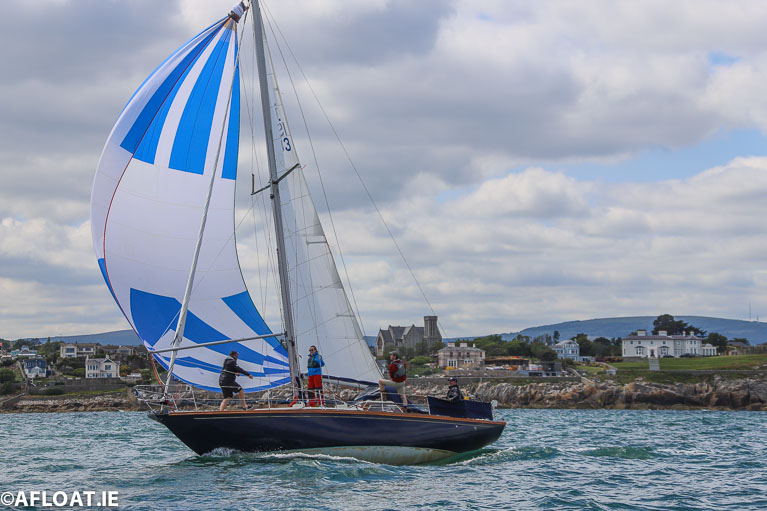

The sunshine and summery sailing has suited the Frazer Meredith syndicate in the Sonata Asterix, they’ve taken the overall lead of IRC4 at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta from Abersoch’s Jonathan Fawcett with the She 31B She Too, with Michal Matulka in the Trapper 300 Eleint (DMYC) staying in third.
The Bullet is Bitten Out of Sight in IRC Non-Spinnaker 1 at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta
Colm Bermingham’s Elan 333 Bite the Bullet from Howth was looking good last night, now he seems unassailable at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta, being in the luxurious position of discarding a second in today’s second race. Terry Fair’s Sigma 33 Cariad from Ballyholme is second, but at 16 points to Bite the Bullet’s 5, the final result seems inescapable, while Eamonn Doyle & Peter O’Toole (Lawrence of Arabia how are you?) have brought their Dehler 36 Shearwater (RStGYC) up to third overall.
History in the making for special Contessa 32 in IRC Non-spinnaker 2
The Contessa 32 is quite a special classic, but Paul Conway’s Cevantes is special and then some, as she is a one-off version with a smaller coachroof – most elegant it looks too. He still leads Non-spin 2 despite having to take a second today (his discard), the Super Seal Gung-Ho (Grainne & Sean O’Shea) continues second overall after a win today, while the UFO 31 Menapia (James & Susan McSweeney, RStGYC) is third.
“Champagne sailing” is a choice expression which is in danger of being over-used every time a bit of sunshine happens upon a decent sailing breeze during race time in Ireland writes W M Nixon. But we’ve no doubt it was being bandied about at some stage on most of the 498 boats taking part in the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta 2019’s third day’s racing on this very special Saturday.
So at the very least, we’ll allow that there was a Bollinger Breeze on the Bay, and if you were on one of the many boats doing well in the two dozen-plus classes, “champagne sailing” is definitely a permitted phrase.
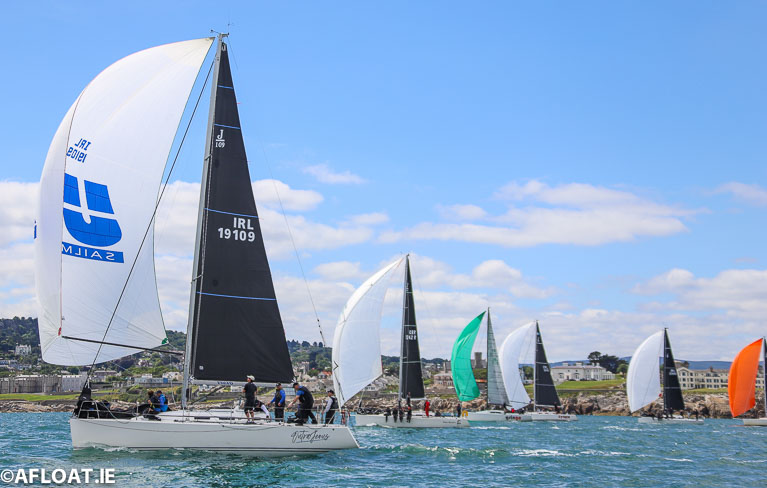 Class One head downwind past Dalkey in today's Coastal Race
Class One head downwind past Dalkey in today's Coastal Race
The sun was around most of the time, obscured occasionally only by the most harmless of clouds, and while the very usable breeze was west of north in the inner bay, it definitely had a growing touch of nor’east to it as you got seaward, and the salty aroma of the real sea with it
 Class One Rounds the Muglins Rock
Class One Rounds the Muglins Rock
This was very much to the benefit of the grand fromages in Classes 0 and 1, and the IRC Coastal Classes as well, for at some stage all were favoured with a cracking beat out to the North Burford Buoy. This workaday navigation marker played such a useful role in the day’s sailing that if it hadn’t existed, then someone would have had to invent it as the programme swung into action. And to round out the sport, the directness of the breezes in through the harbour mouth permitted in-harbour finishes which brought that classic Beechey painting of the Royal St George Regatta of 1874 gloriously back to life, so all was well with the world.
 The Coastal Course Classes reach 'Bray Outfall' mark
The Coastal Course Classes reach 'Bray Outfall' mark
Effectively, tomorrow’s final races will all be done and dusted around lunchtime or very soon after to allow the marathon prizegiving ceremony the time and space it needs, so this evening we’re getting very close to seeing the final lineup for the silverware, and in a couple of classes it’s already all over bar the shouting.
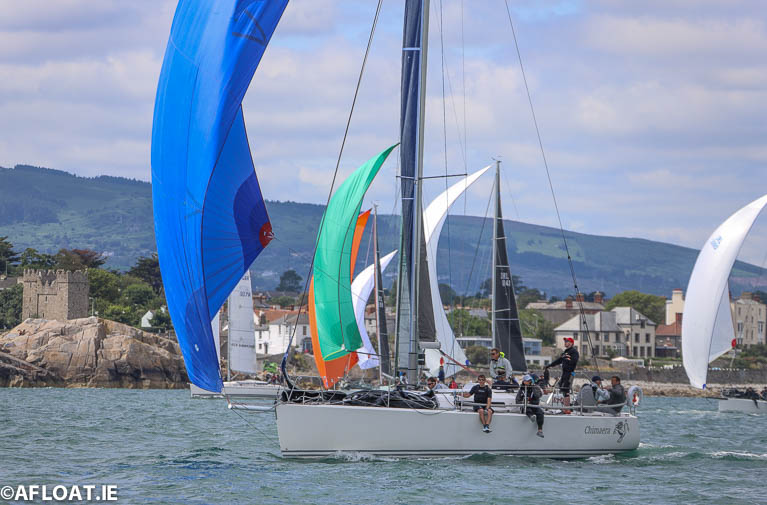 Andrew Craig's J109 Chimaera got away great in the running start (it must be those new spinnaker sheets)
Andrew Craig's J109 Chimaera got away great in the running start (it must be those new spinnaker sheets)
The oven is turned way up among the profusion of J/109s in Class 1. Overnight leader Outrajeous (Richard Colwell & Johnny Murphy, Howth YC) logged a third today, but this has her only one point – at 8 - ahead of John Maybury’s Joker II (RIYC) which managed a first to total 9, while the Goodbody family in White Mischief are on 10 and Pat Kelly’s Storm is in fourth on 11.
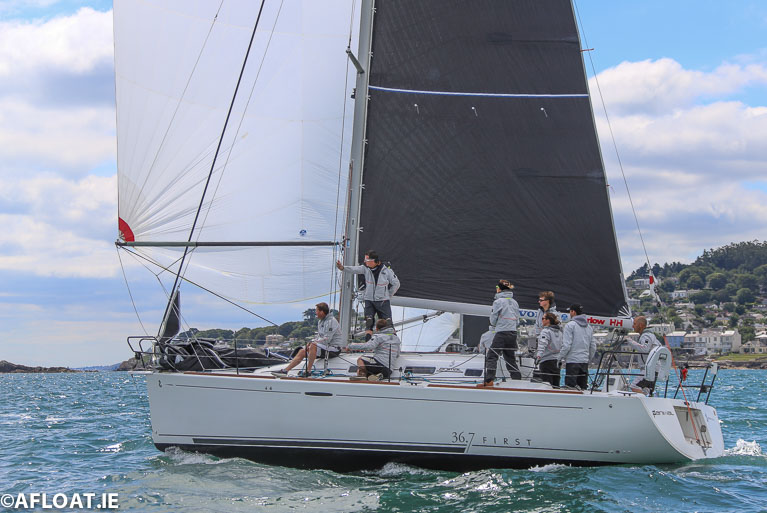 Debbie Aitken’s First 36.7 Animal
Debbie Aitken’s First 36.7 Animal
Storm continues to have a clear lead in the RC 35 sub-division, with Brian and John Hall’s Something Else still second while Debbie Aitken’s First 36.7 Animal is also something else, she manages to hold third after a 5th today despite having J/09s every which way around her.
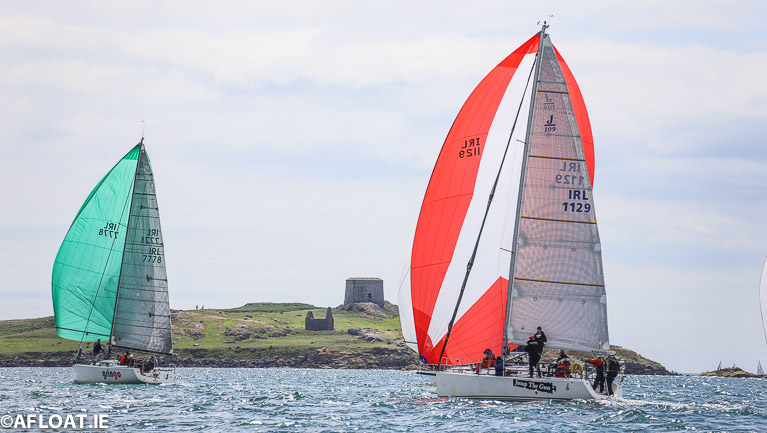

'F’n Gr8' Leads But There's Complex Challenges Among the Quarter Tonners at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta
We concluded yesterday’s racing IRC3 racing at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta with Rory Fekkes’ turbo-powered First 8 F’n Gr8 from Carrickfergus in the overall lead, but things today weren’t so clearcut today among the Quarter Tonners and their assorted sparring partners.
For although F’n Gr8 still leads with 13 points to the 24 of Ken Lawless’s Cartoon (RIYC), the discarding of a 7th and an 18th by the front runner tells its own story.
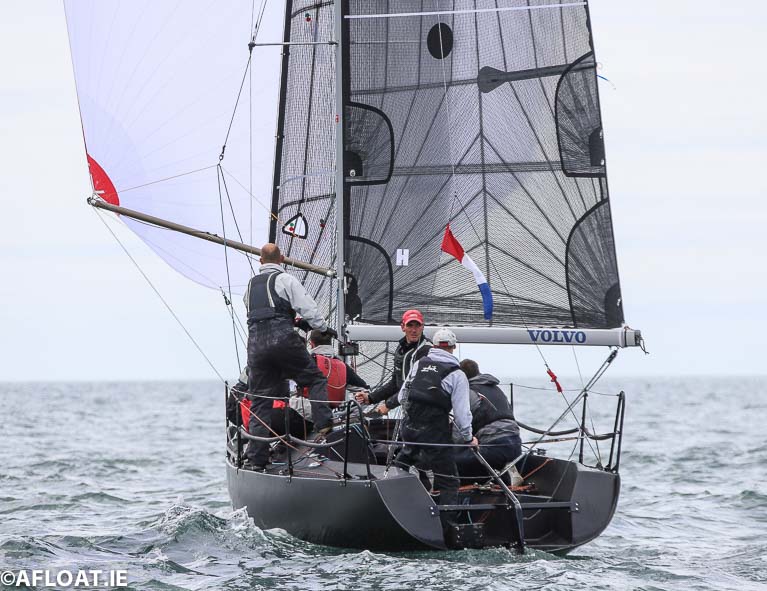 F’n Gr8 still leads with 13 points
F’n Gr8 still leads with 13 points
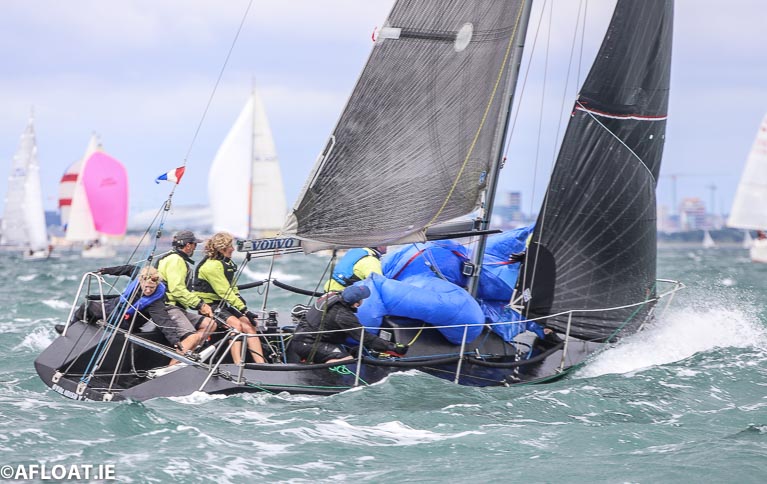 Cartoon is in second overall
Cartoon is in second overall
Third is Brendan Foley's Impala Running Wild and Ger O’Sullivan of Howth with the Formula 28 Animal is fourth, but the real star of today’s racing is Flor O’Driscoll of Bray SC, with a couple of firsts in his J/24 Hard on Port moving him up to fifth overall.
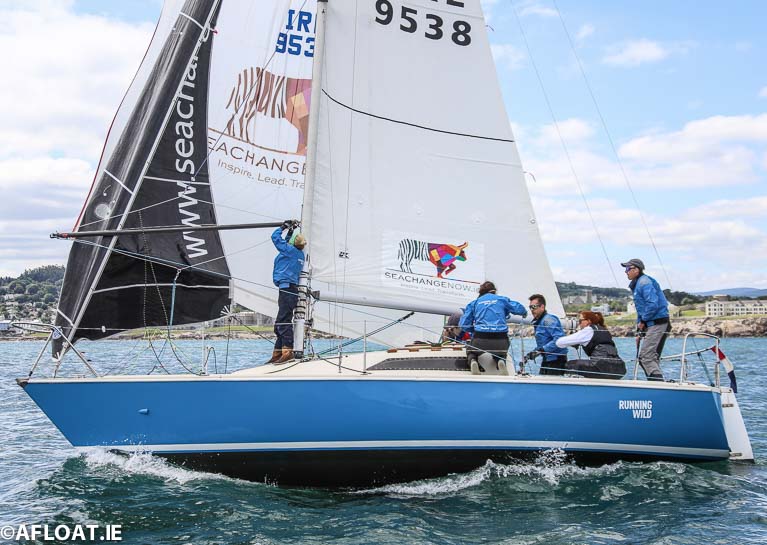 Brendan Foley’s Running Wild is third
Brendan Foley’s Running Wild is third
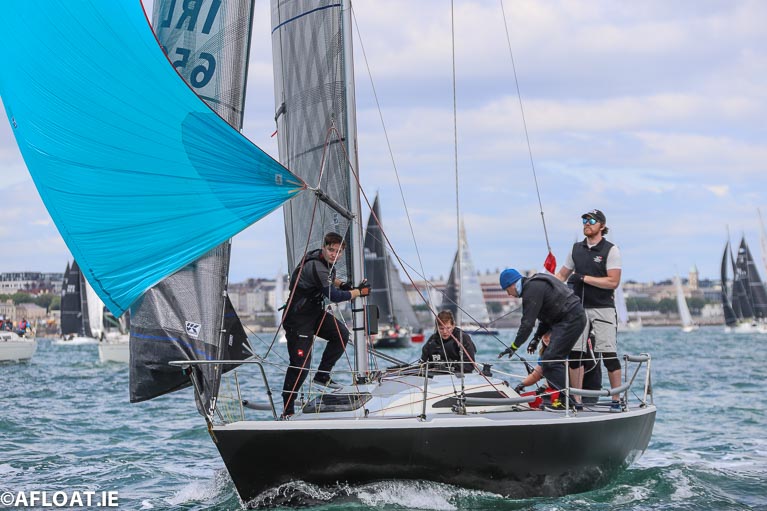 Ger O’Sullivan's Formula 28, Animal is fourth
Ger O’Sullivan's Formula 28, Animal is fourth
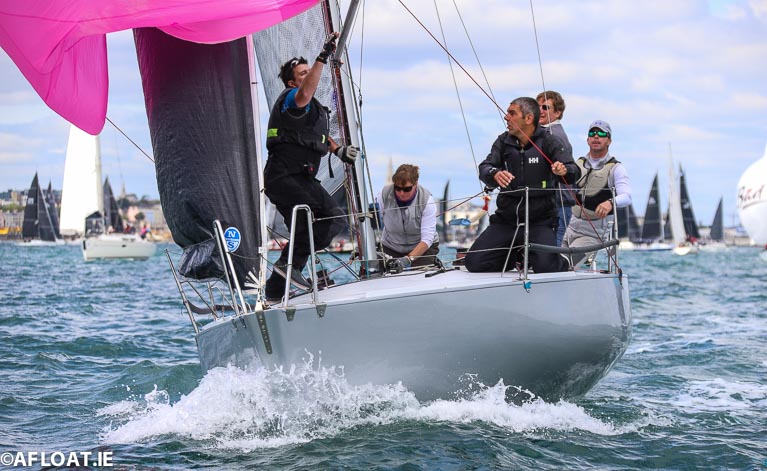 Paul Colton's Cri Cri from the Royal Irish
Paul Colton's Cri Cri from the Royal Irish